berk
Member
- Joined
- Dec 28, 2019
- Messages
- 320
You probably know L-tryptophan as an essential amino acid which helps you sleep better and lightens your mood. It seems that the same L-tryptophan might also improve body composition: an animal study published in Amino Acids by nutritionists from Nanchang University suggests this.
Trytophan is a precursor of serotonin and melatonin, but also plays an as yet not completely understood role in the synthesis of proteins in the body. The Chinese attempted to gain more understanding of this role by performing an experiment in which they gave adult rats a daily oral dose of 200 mg L-tryptophan per kg bodyweight for a week. The human equivalent of this dose would be about 2-3 g per day.
Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. - PubMed - NCBI
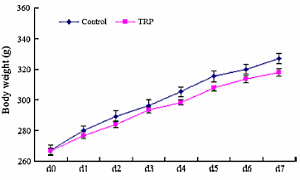
During this period these rats lost a little weight compared with the rats in a control group, which had been given no supplements.
Protein metabolism
The researchers found indications of increased protein synthesis in the rats' blood, such as a decrease in the concentration of isoleucine and valine. These amino acids are important building blocks for muscle tissue.
One possible mechanism is that tryptophan induces the small intestine to absorb more amino acids, the Chinese believe. The rats' small intestine became longer and gained more folds as a result of supplementation. But how extra tryptophan speeds up muscle protein synthesis is still not clear.
Fat metabolism
The Chinese do not report whether the rats' muscles became larger or stronger. What they do say is that L-tryptophan reduced the animals' fat mass, although they do not say by how much. Instead they do provide information on the way in which the amino acid probably boosted the burning of fatty acids.
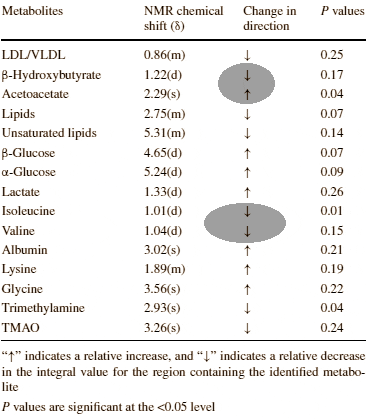
"We found that tryptophan supplementation affected lipid metabolism, leading to reduced fat deposition in the body of tryptophan supplemented group, compared with the control group", the researchers write. "Both acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate are products of fatty acid oxidation in liver, and the ratio of acetoacetate to hydroxybutyrate is an indicator of cytosolic and mitochondrial redox states."
"In this study, tryptophan supplementation increased the level of acetoacetate and decreased the level of beta-hydroxybutyrate in serum, thus elevated the ratio of acetoacetate to beta-hydroxybutyrate. The result suggested that tryptophan supplementation promoted the oxidation of fatty acid."
"So it would lead to a reduced availability of fatty acids for the synthesis of lipids, LDL and VLDL in the body. In support of this view, tryptophan supplementation decreased the serum concentrations of lipids, unsaturated lipids, LDL and VLDL in tryptophan supplemented group rats compared to the control group rats."
Source:
Amino Acids. 2014 Dec;46(12):2681-91.
Trytophan is a precursor of serotonin and melatonin, but also plays an as yet not completely understood role in the synthesis of proteins in the body. The Chinese attempted to gain more understanding of this role by performing an experiment in which they gave adult rats a daily oral dose of 200 mg L-tryptophan per kg bodyweight for a week. The human equivalent of this dose would be about 2-3 g per day.
Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. - PubMed - NCBI
During this period these rats lost a little weight compared with the rats in a control group, which had been given no supplements.

Protein metabolism
The researchers found indications of increased protein synthesis in the rats' blood, such as a decrease in the concentration of isoleucine and valine. These amino acids are important building blocks for muscle tissue.
One possible mechanism is that tryptophan induces the small intestine to absorb more amino acids, the Chinese believe. The rats' small intestine became longer and gained more folds as a result of supplementation. But how extra tryptophan speeds up muscle protein synthesis is still not clear.
Fat metabolism
The Chinese do not report whether the rats' muscles became larger or stronger. What they do say is that L-tryptophan reduced the animals' fat mass, although they do not say by how much. Instead they do provide information on the way in which the amino acid probably boosted the burning of fatty acids.

"We found that tryptophan supplementation affected lipid metabolism, leading to reduced fat deposition in the body of tryptophan supplemented group, compared with the control group", the researchers write. "Both acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate are products of fatty acid oxidation in liver, and the ratio of acetoacetate to hydroxybutyrate is an indicator of cytosolic and mitochondrial redox states."
"In this study, tryptophan supplementation increased the level of acetoacetate and decreased the level of beta-hydroxybutyrate in serum, thus elevated the ratio of acetoacetate to beta-hydroxybutyrate. The result suggested that tryptophan supplementation promoted the oxidation of fatty acid."
"So it would lead to a reduced availability of fatty acids for the synthesis of lipids, LDL and VLDL in the body. In support of this view, tryptophan supplementation decreased the serum concentrations of lipids, unsaturated lipids, LDL and VLDL in tryptophan supplemented group rats compared to the control group rats."
Source:
Amino Acids. 2014 Dec;46(12):2681-91.
Last edited:
